Blog
May 8th Current Affairs
- May 8, 2021
- Posted by: admin
- Category: Culture Current Affairs Daily News Defense & Security Disaster Management Economy Education Environment & Ecology Ethics Geography Governance Health History International Relation Persons in News Polity Science & Technology Social Issues Sports Uncategorized UPSC Notification Videos
1.National Financial Reporting Authority

IN NEWS:
Publication of provisional database for the companies under the regulatory ambit of National Financial Reporting Authority.
KEY HIGHLIGHTS:
- The National Financial Reporting Authority is a regulatory body set up under Section 132 of the Companies Act to oversee compliance with Accounting and Auditing Standards by companies that can be described as Public Interest Entities (PIEs).
- This group includes all listed companies, and large unlisted companies.
- To discharge this mandate, NFRA is in the process of creating a verified and accurate database of companies and auditors that come under the regulatory ambit of NFRA.
- Establishment of this data base involves critical steps like identification and verification of the primary data source, and reconciliation of data (such as Company Identification Number (CIN) which is dynamic) from different sources.
- In this regard the NFRA has been engaging with the Corporate Data Management (CDM) division of Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) and three recognised stock exchanges in India.
- To achieve the objectives for which NFRA has been established, and to promote transparency in its working, this provisional data as of 31st March 2019 has been published on the website of the NFRA (https://www.nfra.gov.in/nfra_domain).
- This provisional data will be updated/revised going forward based on the collection of further data and information.
SOURCE:PIB
2. Reduce human-caused methane emissions by 45% to avoid worst of climate change: UN

IN NEWS:
- Recently, a report, titled Global Methane Assessment: Benefits and Costs of Mitigating Methane Emissions suggested that the world needs to dramatically cut methane emissions to avoid the worst of climate change.
- The report was released by the Climate and Clean Air Coalition and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
Key Highlights:
- Human-caused methane emissions must be cut by 45 per cent to avoid the worst effects of climate change, a new United Nations report has said.
- The report, titled Global Methane Assessment: Benefits and Costs of Mitigating Methane Emissions was released by the Climate and Clean Air Coalition and the United Nations Environment Programme.
- Such a cut would prevent a rise in global warming by up to 0.3 degrees Celsius by 2045, the report added. It would also prevent 260,000 premature deaths, 775,000 asthma-related hospital visits annually, as well as 25 million tonnes of crop losses.
- Human-caused methane emissions are increasing faster currently than at any other time since record-keeping began in the 1980s.
- The report said this was a cause of concern as methane was an extremely powerful greenhouse gas. It was responsible for about 30 per cent of warming since pre-industrial times.
SOURCE:DTE
3. Stress Resolution Framework 2.0 for Individuals, Small Businesses and MSMEs

In news
RBI has announced following set of measures to relieve stress faced by most vulnerable categories of borrowers – individuals, borrowers and MSMEs.
Key takeaways
- Individuals, borrowers and MSMEs with aggregate exposure up to Rs. 25 crore, who have not availed restructuring under any previous frameworks, but classified as standard on 31 March, 2021, will be eligible to be considered under Resolution Framework 2.0.
- This can be invoked till September 30, 2021 and will have to be implemented within 90 days after invocation.
- For individuals and small businesses who have availed restructuring of loans under Resolution Framework 1.0, where moratorium of less than 2 years was permitted, lending institutions can now increase the period and/or extend residual tenure up to a total period of 2 years.
- In respect of small businesses and MSMEs restructured earlier, lending institutions are now permitted to review working capital sanction limits, as a one-time measure.
SOURCE:IE
4. 2DG- DRDO’s Anti-Covid Drug gets nod
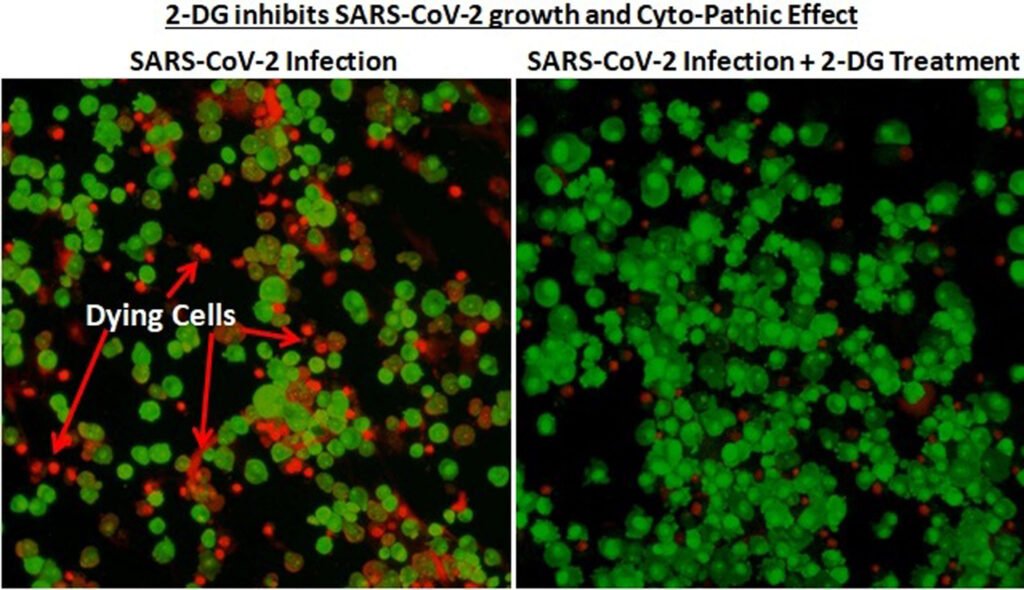
IN NEWS:
The Drugs Controller General of India recently approved an oral drug to treat COVID-19 called the 2-DG.
KEY HIGHLIGHTS:
- The 2-DG was developed by the Defence Research Development Organisation for Emergency Use. 2-DG is 2-Deoxy – D – Glucose. It was developed in collaboration with Dr Reddy’s Laboratories.
- The drug ensures faster recovery of hospitalised patients and will reduce supplemental oxygen dependence during clinical trials.
- It accumulates in infected cells and stops viral synthesis. This accumulation makes the drug unique.
- The drug comes in a powdered form in sachets. It is consumed orally after dissolving in water.
- It was developed by Institute of Nuclear Medicine and Allied Sciences (INMAS). INMAS is a laboratory operating under DRDO.
- The DGCI has granted permission for emergency use of the drug in moderate to severe COVID-19 patients.
- 2-DG is a generic molecule and thus can be easily produced and made available in plenty in the country.
How are 2-DG accumulated in the cells?
- The 2-DG is a glucose molecule. It cannot undergo further glycolysis. Glycolysis is the process in which free energy is released.
- The 2-DG molecules are up taken by the glucose transporters of the cell. The glucose transporters are membrane proteins that facilitate the transport of glucose across plasma membrane.
- This is how the drug reaches the cells. As it cannot undergo glycolysis it simply stays in the cells. Continuous intake of the drug thus leads to accumulation in the cell.
2-DG as Tumour therapeutic
The cancer cells have higher glucose uptake. Thus, when 2-DG is injected into cancer patients, it acts as a good marker for cancer cells.
SOURCE:IE
